Dollar Spot Alert
go.ncsu.edu/readext?474945
en Español / em Português
El inglés es el idioma de control de esta página. En la medida en que haya algún conflicto entre la traducción al inglés y la traducción, el inglés prevalece.
Al hacer clic en el enlace de traducción se activa un servicio de traducción gratuito para convertir la página al español. Al igual que con cualquier traducción por Internet, la conversión no es sensible al contexto y puede que no traduzca el texto en su significado original. NC State Extension no garantiza la exactitud del texto traducido. Por favor, tenga en cuenta que algunas aplicaciones y/o servicios pueden no funcionar como se espera cuando se traducen.
Português
Inglês é o idioma de controle desta página. Na medida que haja algum conflito entre o texto original em Inglês e a tradução, o Inglês prevalece.
Ao clicar no link de tradução, um serviço gratuito de tradução será ativado para converter a página para o Português. Como em qualquer tradução pela internet, a conversão não é sensivel ao contexto e pode não ocorrer a tradução para o significado orginal. O serviço de Extensão da Carolina do Norte (NC State Extension) não garante a exatidão do texto traduzido. Por favor, observe que algumas funções ou serviços podem não funcionar como esperado após a tradução.
English
English is the controlling language of this page. To the extent there is any conflict between the English text and the translation, English controls.
Clicking on the translation link activates a free translation service to convert the page to Spanish. As with any Internet translation, the conversion is not context-sensitive and may not translate the text to its original meaning. NC State Extension does not guarantee the accuracy of the translated text. Please note that some applications and/or services may not function as expected when translated.
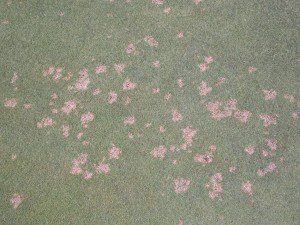
Collapse ▲Over the past couple of weeks, a very familiar turfgrass disease, dollar spot, has begun its assault across much of North Carolina. We have observed this disease on creeping bentgrass putting greens and fairways (mountains).
The dollar spot fungus begins to grow and infect susceptible grasses in the spring when night temperatures exceed 50°F, even though symptoms of the disease may not appear until later in the spring or early summer. In addition, the pathogen requires extended periods of leaf wetness, 10 to 12 continuous hours. Heavy dews that often form during cool nights in the late spring or early summer are most conducive to the disease. Extended periods of wet, overcast weather can also lead to severe dollar spot epidemics on susceptible grasses. Dollar spot remains active throughout the summer in many areas, but disease activity typically slows when high temperatures consistently exceed 90°F.
Turfgrasses that are deficient in nutrients, especially nitrogen, are more prone to dollar spot and also recover from the damage more slowly than well-fertilized turf. The disease is also encouraged by drought stress, low mowing, excessive thatch accumulation, frequent irrigation, and low air movement. Certain cultivars of creeping bentgrass, perennial ryegrass, and Kentucky bluegrass are very susceptible to dollar spot, while others are fairly tolerant.
For more information, including control recommendations, please review our dollar spot control recomendations.